Ezlo_EP01
Ezlo_EP01 is a low-power embedded Wi-Fi and Bluetooth module that Ezlo has developed. It consists of
a highly integrated chip (ESP32-D0WDQ6), a few peripherals, an embedded Wi-Fi network protocol stack,
the Bluetooth LE network protocol, and varied library functions
1.Overview
The Ezlo_EP01 is a versatile Wi-Fi+Bluetooth®+Bluetooth LE MCU designed for a wide range of
applications, from low-power networked sensors to the most challenging tasks such as voice encoding,
music streaming and MP3 decoding. This module is based on the ESP32-D0WDQ6* chip. The embedded
chip is designed to scale and adapt.
| CPU and OnChip Memory |
CrystalOscillators
Themoduleusesa40-MHzcrystaloscillator |
|
|
| ESP32-U4WDH embedded, Xtensa dual-core |
Wi-Fi |
| 32-bit LX6 microprocessor, up to 240 MHz |
802.11b/g/n |
| 448 KB ROM |
Bit rate: 802.11n up to 150 Mbps |
| 520 KB SRAM |
A-MPDU and A-MSDU aggregation |
| 16 KB SRAM in RTC |
0.4 µs guard interval support |
| 128M-BIT SPI flash |
Center frequency range of operating channel: |
|
2412 ~ 2484 MHz |
| Operating Conditions |
Bluetooth |
|
Bluetooth v4.2 BR/EDR and Bluetooth LE |
| Operating voltage/Power supply: 3.0 ~ 3.6 V |
specification |
| Operating ambient temperature: |
Class-1, class-2, and class-3 transmitter |
| – 85 °C version module: –40 ~ 85 °C |
AFH |
| – 105 °C version module: –40 ~ 105 °C |
CVSD and SBC |
|
CVSD and SBC |
| Antenna Options |
|
| ESP32: On-board PCB antenna |
|
2. Module interfaces
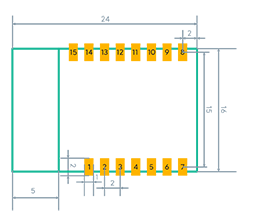
2.1 Dimensions and footprint
Ezlo_EP01 has two rows of pins with a 2 ±0.1 mm pin spacing. The Ezlo_EP01 dimensions are 16 mm (W)×24
mm (L) ×1.2 mm (H). The diagram of dimensions
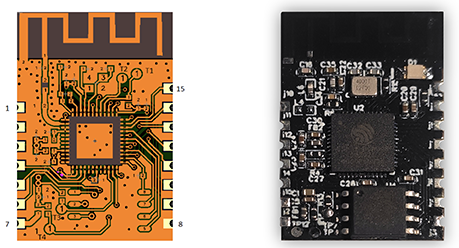
2.2 Pin definition
| 1 – Gpio21 |
(ADC AI) |
| 2 – En |
(I – Enabling pin, which needs to be connected to the voltage of 3.3V in normal cases and corresponds to CHIP_EN) |
| 3 – Gpio25 |
(I/O – Common IO pin) |
| 4 – Gpio26 |
(P – Support hardware PWM) |
| 5 – Gpio27 |
(I/O – Support hardware PWM and Common IO pin) |
| 6 – Gpio16 |
(I/O – Support hardware PWM and Common IO pin) |
| 7 – Power+3,3V |
(P – Power supply source (3.3V)) |
| 8 – Gnd |
(P – Power supply reference ground) |
| 9 – Gpio19 |
(O – Common IO pin) |
| 10 – Gpio22 |
(O – Common IO pin) |
| 11 – Gpio4 |
(I/O – Common IO pin) |
| 12 – Gpio17 |
( I/O – Support hardware PWM and Common IO pin) |
| 13 – Gpio23 |
( I/O – Support hardware PWM and Common IO pin) |
| 14 – Rx1 |
(I/O – UART0_RXD) |
| 15 – Tx1 |
(I/O – UART0_TXD) |
3. Electrical parameters
3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
| Parameter |
Description |
Min |
Max |
Unit |
| VDDA, VDD3P3, VDD3P3_RTC,
VDD3P3_CPU, VDD_SDIO |
Allowed input voltage |
–0.3 |
3.6 |
V |
| Ioutput |
Cumulative IO output current(1) |
— |
1200 |
mA |
| TSTORE |
Storage temperature |
–40 |
150 |
°C |
*The product proved to be fully functional after all its IO pins were pulled high while being connected to
ground for 24 consecutive hours at ambient temperature of 25 °C.
Recommended Power Supply Characteristics
| Parameter |
Description |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
| VDDA, VDD3P3_RTC ,
VDD3P3, VDD_SDIO (3.3 V mode) |
Voltage applied to power supply pins per power domain |
2.3/3.0 |
3.3 |
3.6 |
V |
| VDD3P3_CPU |
Voltage applied to power supply pin |
1.8 |
.3.3 |
3.6 |
V |
| IVDD |
Current delivered by external power supply |
0.5 |
– |
– |
A |
| T |
Operating temperature |
–40 |
— |
125 |
°C |
3.2 DC Characteristics (3.3 V, 25 °C)
| Parameter |
Description |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
| CIN |
Pin capacitance |
— |
2 |
— |
pF |
| VIH |
High-level input voltage |
0.75×VDD |
— |
VDD+0.3 |
V |
| VIL |
Low-level input voltage |
–0.3 |
— |
0.25×VDD |
V |
| IIH |
High-level input current |
— |
— |
50 |
nA |
| IIL |
Low-level input current |
— |
— |
50 |
nA |
| VOH |
High-level output voltage |
— |
— |
— |
V |
| VOL |
Low-level output voltage |
— |
— |
0.1×VDD |
V |
| IOH |
| High-level source current |
VDD3P3_CPU power domain |
| (VDD1 = 3.3 V, VOH >= 2.64 V |
VDD3P3_RTC power domain |
| output drive strength set to the maximum) |
VDD_SDIO power omain |
|
|
|
|
|
| IOL |
Low-level sink current (VDD1= 3.3 V, VOL = 0.495 V, output drive strength set to the maximum |
— |
28 |
— |
mA |
| RPU |
Resistance of internal pull-up resistor |
— |
45 |
— |
VkΩ |
| RPD |
Resistance of internal pull-down resistor |
— |
45 |
— |
VkΩ |
| VIL_nRS |
Low-level input voltage of CHIP_ PU to shut down the chip |
— |
— |
0.6 |
V |
3.3 RF Current Consumption in Active Mode Current Consumption Depending on RF Modes
| Work Mode |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
| Transmit 802.11b, DSSS 1 Mbps, POUT = +19.5 dBm |
— |
240 |
— |
mA |
| Transmit 802.11g, OFDM 54 Mbps, POUT = +16 dBm |
— |
190 |
— |
mA |
| Transmit 802.11n, OFDM MCS7, POUT = +14 dBm |
— |
180 |
— |
mA |
| Receive 802.11b/g/n |
— |
95 ~ 100 |
— |
mA |
| Transmit BT/BLE, POUT = 0 dBm |
— |
130 |
— |
mA |
| Receive BT/BLE |
— |
95 ~ 100 |
— |
mA |
3.4 Wi-Fi Radio Characteristics
| Parameter |
Description |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
| Operating frequency range |
— |
2412 |
— |
2484 |
MHz |
| Output impedance |
— |
— |
30+j10 |
— |
Ω |
| TX power |
|
|
|
|
|
| Sensitivity |
| 11b, 1 Mbps |
| 11b, 11 Mbps |
| 11g, 6 Mbps |
| 11g, 54 Mbps |
| 11n, HT20, MCS0 |
| 11n, HT20, MCS7 |
| 11n, HT40, MCS0 |
| 11n, HT40, MCS7 |
|
|
| –98 |
| –88 |
| –93 |
| –75 |
| –93 |
| –73 |
| –90 |
| –70 |
|
|
| dBm |
| dBm |
| dBm |
| dBm |
| dBm |
| dBm |
| dBm |
| dBm |
|
| Adjacent channel rejection |
| 11g, 6 Mbps |
| 11g, 54 Mbps |
| 11n, HT20, MCS0 |
| 11n, HT20, MCS7 |
|
|
|
|
|
4. Antenna
4.1 Antenna type
Ezlo_EP01 uses only an onboard PCB antenna.
4.2 Antenna interference reduction
To ensure optimal Wi-Fi performance when the Wi-Fi module uses an onboard PCB antenna, it is recommended that the antenna be at least 15 mm away from other metal parts.
To ensure antenna performance, the PCB should not be routed or clad with copper in the antenna area.
The main points of the layout: Make sure that there is no substrate medium directly below or above the
printed antenna.
Make sure that the area around the printed antenna is far away from the metal copper skin,
so as to ensure the radiation effect of the antenna to the greatest extent
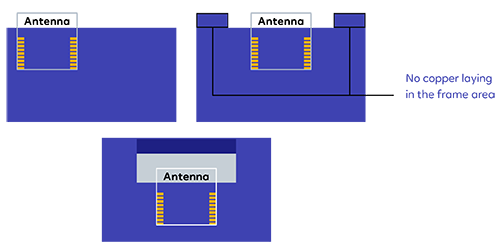
5 Recommended PCB layout
6 Power-on sequence and resetting
6.1 Treatment of GPIO pins
A few pins of the module will have instantaneous high-level pulses before the chip fully works, and
everything will be normal after the chip works. For these pins, if they are directly used as driving light
sources or relays, in order to avoid the effect of burrs at the moment of power-on, refer to the following
processing methods: Pull down a 1-KΩ resistor at an output port of a pin, and then connect a diode in
series.
At this time, the voltage of a GPIO will drop to about 2.7V after passing through the diode. The red box
represents the original drive tube on the customer’s baseboard. A diode D1 and pull-down 1-KΩ resistor
need to be added. If a lamp is directly driven, pull down a 10-KΩ resistor on the grid of the positive Mos.
If a lamp is not directly driven and a PWM signal will not be sent until the module is officially launched,
there is no need to add a pull-down resistor and diode. If a relay is driven, you can change the diode to
a resistor of 0 Ω according to the actual situation.
6.2 Storage Conditions
The products sealed in moisture barrier bags (MBB) should be stored in a non-condensing atmospheric
environment of ∠ 40 °C and 90%RH. The module is rated at the moisture sensitivity level (MSL) of 3.
After unpacking, the module must be soldered within 168 hours with the factory conditions 25 ± 5 °C and
60 %RH. If the above conditions are not met, the module needs to be baked.
6.3 Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
- Human body model (HBM): ±2000 V
- Charged-device model (CDM): ±500 V
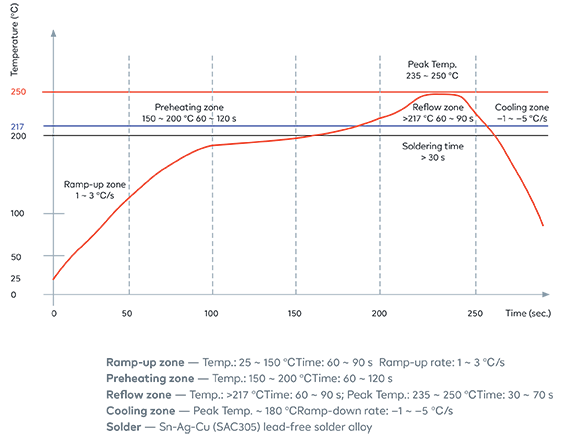
6.4 Reflow Profile
Solder the module in a single reflow
6.5 Ultrasonic Vibration
Avoid exposing Ezlo_EP01 modules to vibration from ultrasonic equipment, such as ultrasonic welders or
ultrasonic cleaners. This vibration may induce resonance in the in-module crystal and lead to its
malfunction or even failure. As a consequence, the module may stop working or its performance may
deteriorate